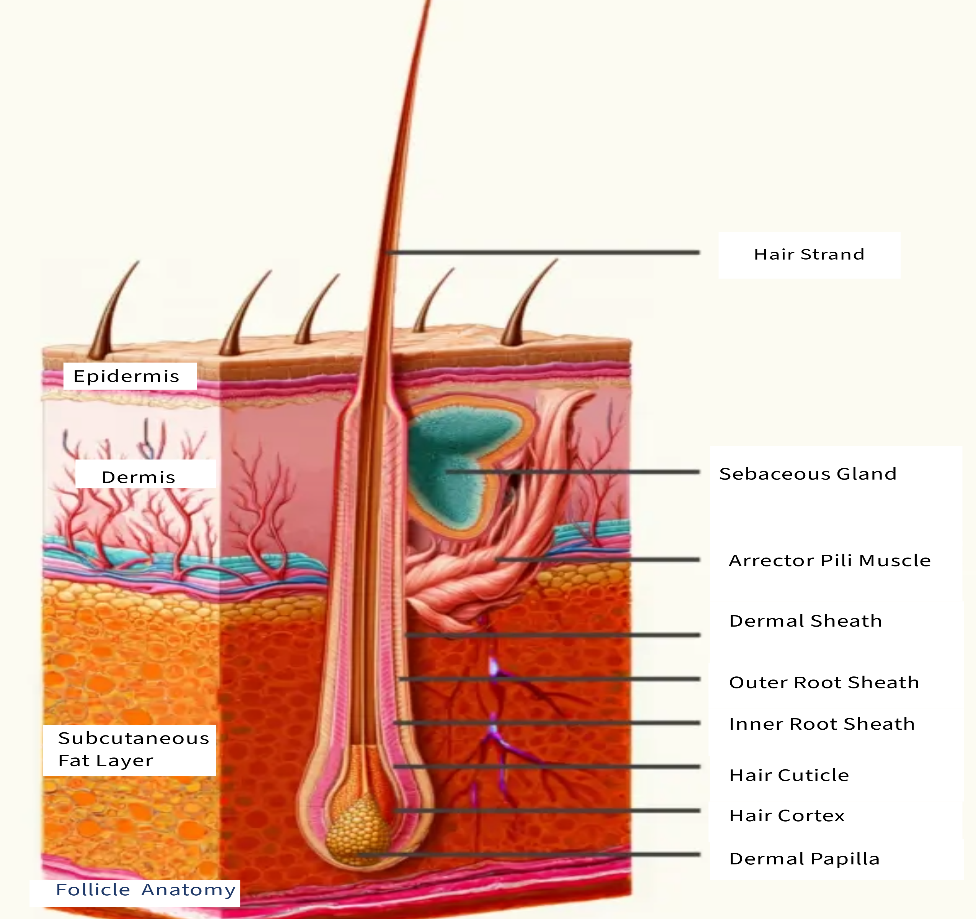
Understanding the Anatomy of the Hair Follicle
The hair follicle is a complex structure located in the dermis of the skin. It is responsible for producing and anchoring the hair. This intricate anatomy supports hair growth throughout the hair cycle phases.
The Hair Shaft;
Cuticle: The cuticle is the outermost layer of the hair made of overlapping cells that protect the hair and adds to its tensile strength.
Cortex: the cortex is a thicker middle layer containing keratin and the pigment melanin. This layer gives the hair its strength and texture. It also contains melanin which gives the hair it colour.
Medulla: the medulla is the innermost layer and is present in only some types of hair. The medulla provides structural support.
The Follicular Structure;
Infundibulum: This is the upper portion of the follicle that opens up to the skin surface it includes the sebaceous gland ducts. A blockage in this area can cause an ingrown hair.
Isthmus: The middle section of the hair follicle itself is called the isthmus. It is located between the sebaceous gland duct and the bulge region of the follicle.
Bulge: The bulge is a shallow recess filled with stem cells and is located in the outer root sheath of the follicle. These stem cells are essential for hair growth and follicular regeneration.
Bulb: The bulb is the enlarged base of the hair follicle which contains cells that divide to produce the hair shaft.
Outer Root Sheath: The outer root sheath is a protective layer that extends from the epidermis and surrounds the hair follicle.
Inner Root Sheath: The inner root sheath lies beneath the outer root sheath and helps guide and shape the growing hair shaft.
Dermal Papilla: Dermal Papilla are found at the base of the follicle bulb. They are a cluster of specialized cells containing blood vessels that supplies the blood and vital nutrients relaying the chemical signals that regulate the hair growth cycles.
Sebaceous Glands: The sebaceous gland is attached to the follicle. Its function is to secrete sebum (oil) to lubricate the hair and surrounding skin.
Arrector Pili Muscle: The erector pili muscle is a smooth muscle connected to the follicle. It contracts in response to cold or fear causing the hair to stand on end.
Blood Supply and Nerves: The hair follicle is nourished by a rich capillary network around the dermal papilla. It is packed with sensory nerves. This allows it to be sensitive to touch and pain.